Farasan Islands
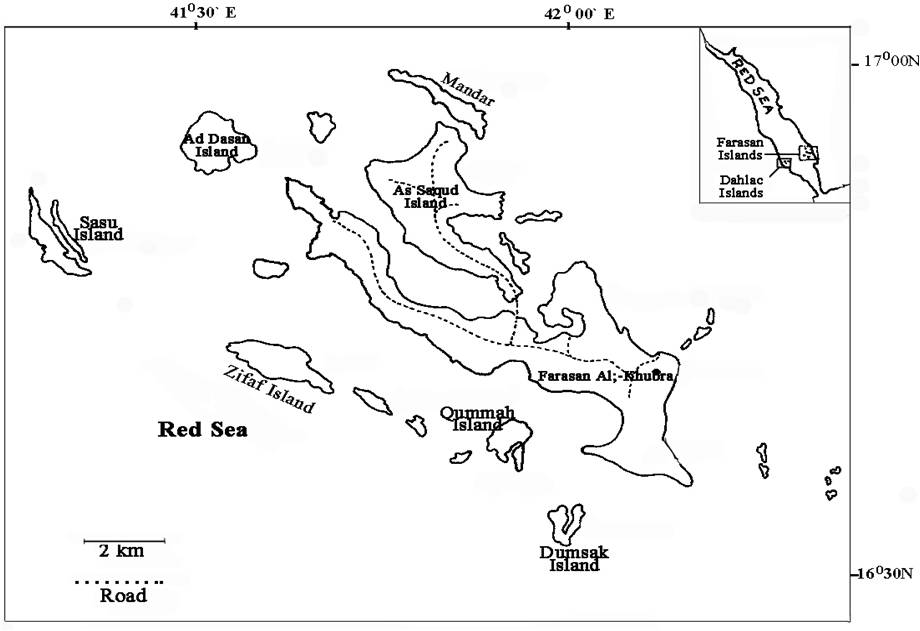
Farasan archipelago, lies in the southern part of Red Sea (160 20` -170 20` N, 410 24`-420 26` E), is about 40 km. away from the Jizan coast and attains a width of approximately 120 km. in SE to NW direction. Sea in this area is very shallow (c.100 meters) and has a width of approximately 360 km. between Jizan coast and the corresponding coast in Eritrea. The group consists of some 176 low coral islands. Among these only 36 or so islands, consisting of both big and small islands, are seen above sea level. Farasan Al-Kabir (369 sq. km) has the longest perimeter (216 km) and the highest population strength (c. 4500). Other important islands with longest perimeters are Sajid or Saqid (109 sq. km), Qummah (14.3 sq. km) and Zifaf (10 sq. km). The altitude of these islands ranges from 20 to 70 m. The entire region is an uplifted coral reef, and is composed, mainly, of fossil, coral-surfaces along wadis and runnels and eroded coral cliffs or coral sands along coastal regions. However, soil formations like Aeolian and alluvial soil deposits can also be seen in some areas such as in protected bays, sandy shores, etc.
In other areas, especially in Farasan Al-Kabir, long narrow ravines have developed due to the leaching of salt substratum and the collapse of overlying coral surfaces. These ravines are about 50 ft. deep and possess a sizable portion of the floral components, mostly ephemerals. Generally islands consist of uniform reef flat that are underlain by bright white marly limestones. Farther down, these are replaced by yellow-green sequences with isolated clay interlayers. An overall evaluation of the Farasan archipelago, particularly in Farasan Al-Kabir and Sajid, shows that the area has numerous faults and fault bundles. Though there are various speculations about the development of these fault structures, the present day fracturing of the area is apparently due to the ascending salt and so in part to the associated gravitational sliding process. The general topography of other islands such as Zifaf, Dawshak, Dumsuq, etc. are also more or less same as that of Farasan Al-Kabir. However, in Zifaf, the fossil coral is in the form of ridges and folds with a number of wadis.
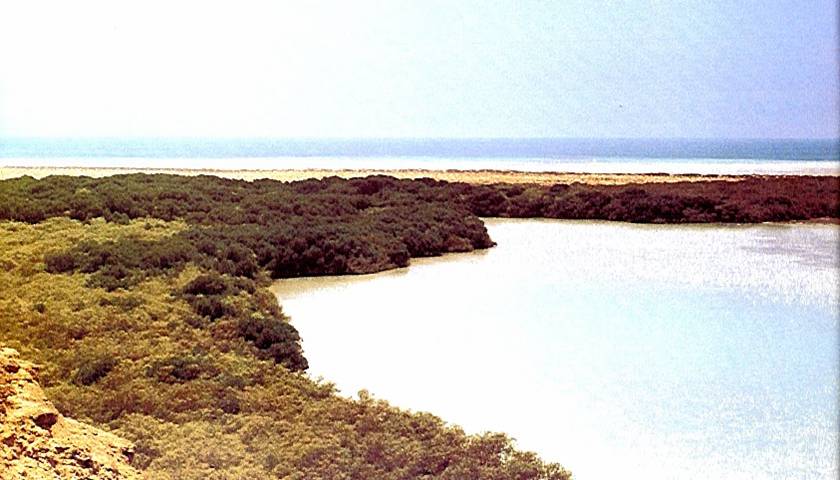

The studies on the flora of Farasan archipelago and various plant communities are of great significance in scientific research as the species occur in an independent environment where influences from other similar communities found in the mainland are almost nil. Presently, Farasan Al-Kabir is a protected area because of the presence of the only remaining wild population of Arabian Gazelle. These islands also play an important role for migratory birds as a nesting place and for developing a conduce environment for a number of endemic races of snakes. However, the first and foremost important factor that makes Farasan group of islands unique is the presence of two important Mangrove populations, Avicennia marina and Rhizophora mucronata. These species are ecologically important and highly productive littoral biotopes and are acting as a reservoir and refuge for many small animals, birds and fish. The pneumatophores that grow erect above water are an ideal site for the breeding of a number of fish, particularly of shrimps, prawns and crabs. Both species share the same shore-line habitat and seen growing side by side. Though intermixed with each other, Rhizophora mucronata can be easily told apart from the other by its shiny, dark green leaves.




Climate
There are no weather stations located in any part of the archipelago. The climatic data is, therefore, collected from Jizan meteorological station. Similar to the climate of Tihama region in the mainland, all islands are also generally dry with unpredictable rain. The data recorded from 1985 to 1998 shows that the highest average precipitation was reported in December and the highest average temperature was in the months of June and August.
Flora and Vegetation
The flora comprises about 200 species of flowering plants in 49 families. Occasional rains, condensation of dews or underground water sources are the main influential factors for the growth of annual vegetation in these islands. The highest concentration of the vegetation is seen in the sheltered wadis with fine silty-clay. The southeastern area of Farasan Al-Kabir, where the land is rugged, contains the highest number of plant species whereas the northwestern unbroken plateau and the western facing shoreline are devoid of plants except for a few annual species. Among the higher plants, a considerable number of them are halophytes or semi-halophytes and the growth of these plants is influenced by the salinity of the soil and the proximity to the seashore. Vegetation along the shoreline of Farasan and Sajid islands, particularly along the inlets and bays is dominated by Avicennia marina whereas in Zifaf and Dumsuq islands another mangrove, Rhizophora mucronata, also show its presence along with Avicennia marina.
The overall vegetation of Farasan Islands is interesting in two aspects: (a) because of its similarity to the distribution of natural plant communities and (b) its similarity to the floral elements of the Tihama Region of the southwestern region of mainland; Saudi Arabia. The plant communities at the south eastern part of the island, where the density of the vegetation is noticeably high, are dominated by small trees and shrubs such as Acacia ehrenbergiana, Commiphora gileadensis and Salvadora persica. Occasionally trees like Hyphaene thebaica and shrubs such as Cadaba glandulosa, Grewia tenax, Indigofera oblongifolia and climbers such as Cissus quadrangularis, Pentatropis nivalis are also present in varying densities. Annuals in this area are, mainly, represented by Zygophyllum simplex, Polycarpaea spicata, Euphorbia granulata and others. At the edges of the ravines where the substrata are somewhat exposed due to erosion, isolated subshrubs such as Aerva javanica, Capparis sinaica and Ochradenus baccatus were present along with a considerable number of annuals.
Overall four sets of distribution patterns can be found in the islands, ranging from a very narrow restricted distributions, such as rare, scattered to dominant or abundant. Apparently, the populations of Acacia ehrenbergiana and Zygophyllum simplex are the most dominant species in the interior regions of the southern parts of Farasan Al-Khubra and other main islands while the populations of Limonium axillare, Halopeplis perfoliata, Zygophyllum coccineum and Suaeda monoica dominate along the coastal and subcoastal regions. The occurrence of grasses are also significant throughout the area. These are mostly represented by Sporobolus helvolus, Dichanthium foveolatum, Panicum turgidum, Hyparrhenia hirta, and Tricholaena teneriffae. In open plains where the plants mainly concentrate in and around small depressions and under the shelters of boulders, the representative ephemerals are Zygophyllum simplex, Eragrostis ciliaris, Amaranthus viridus and others. The sheltered habitats of the inlets and bays, particularly in Farasan Al-Khubra, are calm and allow the free flow of sea-water during high tide. These areas are conducive for the growth and survival of Mangrove species. However, an association of the 2 mangrove species, Avicennia marina and Rhizophora mucronata known to occur was not encountered at the inlets along the south eastern coastal regions of Farasan Al-Khubra. It is probably due to large scale urbanization and the construction of a new port in the vicinity of mangrove habitats.
Sasid (Sajid or Saqid) Island, the second largest Island in the Archipelago is also an open flat reef with shallow wadis. Vegetation of this island is dominated by halophytic communities such as Limonium axillare, Suaeda monoica and occasional trees such as Hyphaene thebaica. Abandoned agriculture lands are a common sight on this island especially near old dwellings. The commonest species at these locations in order of abundance are: Acacia ehrenbergiana, Commiphora giladensis, Indigofera oblongifolia, Grewia tenax, Capparis sinaica, Indigofera spinosa, Aerva javanica, Blepharis ciliaris and Dichanthium foveolatum.
Topography of other islands are more or less similar to the two major islands. Broad wadis between the elevated ridges are characteristic of the Zifaf Island. Mangrove populations in this island, represented by both Avicennia marina and Rhizophora mucronata, are dense and rich and not impacted by external influences. Vegetation of the coastal sandy areas, is represented by Limonium axillare and Aeluropus lagopoides; and along the gentle slopes and ridges, the vegetation is dominated by occasional clumps of Commiphora gileadensis, Cocculus pendulus, Aerva javanica and Indigofera oblongifolia. The vegetation of Dawshak and Dumsuq islands are also more or less similar to other smaller islands except for the presence of species such as Commiphora erythraea in the latter island. These two islands are devoid of any inlets favorable for the growth of mangroves, although the presence of mangroves was reported in some works. The terrain of some of the smaller islands (Ra’s Rasib (Mandar), Abu-Tuk) along the northern sides of Sasid Island is, to a certain extent, barren and sparsely vegetated. However, on the northern side of the Ra’s Rasib island, dense communities comprising Limonium axillare, Suaeda vermiculata and Suaeda monoica were recorded.
Following species of Saudi Arabian flora are so far reported from Farasan Archipelago only.
Basilicum polystachion (L.) Moench Labiatae
Cleome noeana ssp. brachystyla Chamberlain & Lamond Capparaceae
Commiphora erythraea (Ehrenb.) Engl. Burseraceae
Dinebra retroflexa (Vahl) Panzer Gramineae
Drake-brockmania somalensis Stapf Gramineae
Euphorbia collenetteae Al-Zahrani & El-Karemy Euphorbiaceae
Ficus populifolia Vahl Moraceae
Glossonema sp. aff. boveanum (Decne.) Decne. Asclepiadaceae
Indigofera semitrijuga Forssk. Leguminosae
Ipomoea hochstetteri House Convolvulaceae
Limonium cylindrifolium (Forssk.) Verdc. Plumbaginaceae
Micrococca mercurialis (L.) Benth. Euphorbiaceae
Nothosaerva brachiata (L.) Wight Amaranthaceae
Taverniera cuneifolia (Roth) Arn. Leguminosae
Vahlia digyna (Retz.) Kuntze Vahliaceae
Following is list of sea grasses reported from the shallow waters of various islands.
Cymodocea rotundata Asch. & Schweinf
Cymodocea serrulata (R.Br.) Asch. & Magnus
Halodule uninervis (Forssk.) Boiss.
Syringodium isoetifolium (Asch.) Dandy
Thalassodendron ciliatum (Forssk.) Hartog
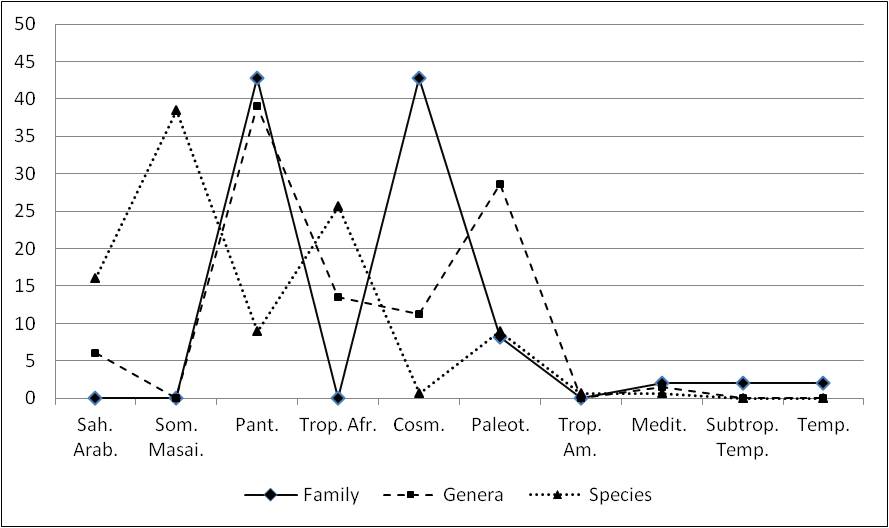
The greatest association of the flora of Farasan Islands is with the Somalia-Masai phytogeographical region (38.46%), followed by Tropical African (25.64%), Saharo-Arabian (16.02%) and others (19.88%). As far as the endemism is concerned, the study area of less than 600 sq km comprises 5 regional endemics (2.5%) compared to 2.82% for Jizan area in the mainland and 10.78% for the whole of mainland Saudi Arabia.
ACANTHACEAE
Barleria hochstetteri Nees
Blepharis ciliaris (L.) B.L. Burtt.
Ecbolium viride Alston
Justicia flava (Vahl) Vahl
AIZOACEAE
Trianthema portulacastrum L.
Trianthema sheilae A.G. Miller
Zaleya pentandra (L.) Jeffrey
AMARANTHACEAE
Aerva javanica (Burm.f.) Juss. ex Schultes.
Amaranthus graecizans L.
Amaranthus viridis L.
Arthrocnemum macrostachyum (Moric) K. Koch.
Atriplex farinosa Forssk.
Atriplex halimus L.
Cornulaca ehrenbergii Asch.
Digera muricata (L.) Mart.
Halopeplis perfoliata (Forssk. ) Bunge ex Asch.
Nothosaerva brachiata (L.) Wight
Suaeda aegyptiaca (Hasselq,) Zoh.
Suaeda monoica Forssk.
Suaeda vermiculata Forssk.
AMARYLLIDACEAE
Pancratium maximum Forssk.
APOCYNACEAE
(including subfamily- Asclepiadoideae)
Calotropis procera (Ait.) Ait.f.
Caralluma retrospiciens (Ehrenb.) N.E. Br.
Caralluma subulata (Forssk.) Decene.
Cryptolluma edulis (Edgew.) Plowes
Glossonema boveanum (Decne.) Decne
Pentatropis nivalis (J.F. Gmel.) D.V. Field & JRI Wood
ARACACEAE
Hyphaene thebaica (L.) Mart
ARISTOLOCHIACEAE
Aristolochia bracteolata Lam.
ASPARAGACEAE
Asparagus flagellaris (Kunth) Bak
Dipcadi erythraeum Webb & Berth.
BORAGINACEAE
Heliotropium longiflorum (Hochst. & Steud.) Jaub. & Spach.
Heliotropium pterocarpum (Hochst. & Steud.) Jaub. & Spach.
Heliotropium ramosissimum (Lehm.) DC.
Heliotropium strigosum Willd.
Heliotropium subulatum (DC.) Vatk
BURSERACEAF
Commiphora erythraea (Ehrenb.) Engl.
Commiphora gileadensis C. Christ.
CAPPARACEAE
Cadaba farinosa Forssk.
Cadaba glandulosa Forssk.
Cadaba longifolia DC.
Cadaba rotundfolia Forssk.
Capparis cartilaginea Decne.
Capparis decidua (Forssk.) Edgew .
Cleome brachycarpa Vahl..
Cleome gynandra L.
Cleome noeana ssp. brachystyla
Maerua crassifolia Forssk. .
CARYOPHYLLACEAE
Polycarpaea repens (Forssk.) Aschers. & Schweinf.
Polycarpaea spicata Wight
CELASTRACEAE
Maytenus parviflora (Vahl) Sebsebe
COMMELINACEAE
Commelina benghalensis L.
Commelina forsskaolii Vahl
COMPOSITAE /ASTERACEAE
Launaea intybacea (Jacq.) Beauverd
Pluchea dioscoridis (L.) DC.
Pulicaria jaubertii Gamal-Eldin
CONVOLVULACEAE
Convolvulus arvensis L.
Convolvulus glomeratus Choisy
Convolvulus pilosellifolius Desr.
Convolvulus rhyniospermus Hochst. ex Choisy
Cressa cretica L.
Ipomoea eriocarpa R.Br.
Ipomoea hochstetteri House
Ipomoea obscura (L,) Ker.-Gawl.
Ipomoea sinensis ssp. blepharosepala (A. Rich.) A. Meeuse
Seddera latifolia Hochst. & Steud.
Seddera virgata Hocst. & Steud.
CUCURBITACEAE
Cucumis melo var. agrestis
Cucumis prophetarum var. prophetarum L.
Kedrostis gijef (J.F. Gmel.) C. Jeffrey
Zehneria anomala C. Jeffrey
CYMODOCEACEAE
Cymodocea rotundata Ehrenb. & Hemprich.
Cymodocea serrulata (R.Br.) Aschers. & Magnus
Halodule uninervis (Forssk.) Aschers
Syringodium isoetifolium (Ashers.) Dandy
Thalassodendron ciliatum (Forssk.) Hartog
CYPERACEAE
Cyperus bulbosus var. bulbosus Vahl
Cyperus jeminicus Rottb.
Cyperus rubicundus Vah.
EUPHORBIACEAE
Acalypha indica L. .
Andrachne aspera var. glandulosa Hochst. ex A. Rich.
Dalechampia scandens var. cordofana (Hochst. ex Webb) Muell.-Arg.
Euphorbia collenetteae Al-Zahrani & El-Karemy
Euphorbia fractiflexa S. Carter & JRI Wood
Flueggea leucopyrus Willd.
Flueggea virosa (Roxb.) ex Willd.) Voigt
Jatropha glauca Vahl
Micrococca mercurialis (L.) Benth.
Phyllanthus maderaspatensis L.
Phyllanthus rotundifolius Klein ex Willd.
LAMIACEAE / LABIATAE
Basilicum polystachion (L.) Moench
Leucas urticifolia (Vahl) R.Br.
Orthosiphon pallidus Royle ex Benth.
LEGUMINOSAE
Acacia ehrenbergiana Hayne
Alysicarpus glumaceus (Vahl) DC. .
Argyrolobium arabicum (Decne.) Jaub. & Spach.
Crotalaria microphylla Vahl
Indigofera coerulea var. coerulea Roxb.
Indigofera hochstetteri Bak.
Indigofera linifolia (L.f.) Retz.
Indigofera oblongifolia Forssk. .
Indigofera semitrijuga Forssk. .
Indigofera spinosa Forssk.
Prosopis juliflora (SW.) DC. .
Rhynchosia minima var. minima (L.) DC.
Rhynchosia pulverulenta var. pulverulenta Stocks.
Senna alexandrina Miller
Senna holosericea (Fresen) Greuter
Taverniera cuneifolia (Roth) Arn.
Taverniera lappacea (Forssk.) DC.
Tephrosia quartiniana Cuf.
Tephrosia subtriflora Hochst. ex Bak.
Tephrosia uniflora ssp. petrosa (Blatt. & Hall.) Gillet & Ali
LYTHRACEAE
Ammannia baccifera L.
MALVACEAE
Abutilon bidentatum A. Rich..
Abutilon fruticosum Guill. & Perr.
Abutilon pannosum (Forst.f.) Schlecht.
Fioria dictyocarpa (Hochst.) Mattei
Hibiscus micranthus L.
Pavonia arabica Hochst. & Steud.
Senra incana Cav.
Subfamily-Grewioideae
Corchorus depressus (L.) Stocks
Corchorus olitorius L.
Corchorus trilocularis L.
Grewia erythraea Schweinf.
Grewia tenax (Forssk.) Fiori .
MENISPERMACEAE
Cocculus pendulus (J.R. & G. Forster) Diels
MOLLUGINACEAE
Mollugo nudicaulis Lam.
MORACEAE
Ficus cordata ssp. salicifolia (Vahl) C.C. Berg.
Ficus glumosa Del.
Ficus popu1ifolia Vahl
NYCTAGINACEAE
Boerhavia dffusa L.
Commicarpus helenae (Roem. & Schultes) Meikle
OROBANCHACEAE
Cistanche tubulosa (Schenk) Wight
Striga gesnerioides (Willd.) Vatke
PLANTAGINACEAE
Lindenbergia indica Vatke
Schweinfturthia pterosperma (A. Rich.) A. Braun
PLUMBAGINACEAE
Limonium axillare (Forssk.) O. Kuntze
Limonium cylindrifolium (Forssk.) O. Kuntze
POACEAE /GRAMINEAE
Aeluropus lagopoides (L.) Trin.
Aristida adscensionis L.
Aristida funiculata Trin. & Rupr.
Brachiaria ovalis Stapf.
Brachiaria ramosa (L.) Stapf
Cenchrus ciliaris L.
Cenchrus setigerus Vahl
Chrysopogon plumulosus Hochst.
Dactyloctenium aegyptium (L.) Willd.
Dactyloctenium aristatum Link.
Dactytoctenium scindicum Boiss.
Dichanthium foveolatum
(Del.) Roberty
Digitaria ciliaris (Retz) Koel.
Dinebra retroflexa (Vahl) Panzer
Drake-Brockmania somalensis Stapf
Elionurus royleanus A. Rich.
Eragrostis lepida (A. Rich.) Hochst. & Steud.
Eragrostis minor Host
Eriochloa fatmensis (Hochst. & Steudel) Clayton
Halopyrum mucronatum (L.) Stapf.
Panicum coloratum L..
Panicum turgidum Forssk.
Paspalidium desertorum (A. Rich.) Stapf
Setaria verticillata (L.) P. Beauv.
Setaria viridis (L.) P. Beauv.
Sporobolus helvolus (Trin.) Dur. & Schinz..
Sporobolus spicatus (Vahl) Kunth
Tetrapogon tenellus (Koenig ex Roxb.) Chiov.
Tricholaena teneriffae (L.f.) Link.
POLYGALACEAE
Polygala erioptera DC.
PORTULACACEAE
Portulaca oleracea L.
RESEDACEAE
Ochradenus baccatus Del.
RHAMNACEAE
Ziziphus spina-Christi var. spina-Christi (L.) Willd.
RHIZOPHORACEAF
Rhizophora mucronata Lam.
RUBIACEAE
Kohautia caespitosa var. caespitosa Schnizl.
SALVADORACEAE
Salvadora persica L.
SCROPHULARIACEAE
Anticharis glandulosa Asch.
SOLANACEAE
Solanum coagulans Forssk.
Solanum forsskaolii Dun.
Solanum surattense Burm.f.
TAMARICACEAE
Tamarix aphylla (L.) Karst.
URTICACEAF
Forsskaolea viridis Ehrenb.
VAHLIACEAE
Vahlia digyna (Retz.) O. Kuntze
VERBENACEAE
Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh.
Chascanum marrubifolium Fenzl ex Walp
Premna resinosa (Hochst.) Schau
Priva cordifolia (L.f.) Druce
VITACEAE
Cissus quadrangularis L.
XANTHORRHOEACEAE
Aloe officinalis Forssk.
ZYGOPHYLLACEAE
Tetraena alba (L.f.) Beier & Thulin
Tetraena simplex (L.) Beier & Thulin
Zygophyllum coccineum var. coccineum L.